CHLOROPHYTUM
Chlorophytum
Ker Gawl., Bot. Mag. 27: t. 1071. 1807; Xinqi &Tamura, Fl. China @ eFloras.org 24: 205; World Flora Online.
Tufted, herbaceous, perennial, rhizomatous, rhizome often short, inconspicuous, sometimes thick, elongate; plant variable in size and robustness, 5-150 cm high. Roots usually +/- thick or slightly fleshy. Aerial stems condensed, leafy. Leaves usually in basal rosettes, sometimes substichous or fasciculate, sessile or petiolate, usually linear to elliptic-lanceolate, conduplicate, base sheathing. Scape axillary, simple or few-branched, proximally with bract-like cauline leaves. Inflorescence a terminal, spicate, racemose or paniculate, flowers in discrete, bracteate clusters of (1-)2-9, bracts small, unequal. Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, hypogynous, open, star-shaped; pedicels mostly articulate near middle. Perianth usually white, sometimes pink, green, yellow or brownish (colour often restricted to stripes on outside), tepals 6, free, 3-7-veined, in 2 whorls, outer tepals narrower than inner, persistent or marcescent. Stamens 6, straight or curved down, free, inserted at base of tepals, shorter than perianth; filaments filiform to fusiform (usually slightly widened in middle), glabrous or minutely papillate; anthers nearly basifixed, introrse, dehiscence by longitudinal slits. Ovary superior, usually sessile, 3-lobed or triquetrous, 3-locular, 1- many ovules per loculus; style straight or declinate, slender; stigma small, punctate to capitate. Fruit a capsule, usually 3-angled, or 3-lobed with 3-valved loculicidal openings. Seeds black or brown, flattened.
202 species
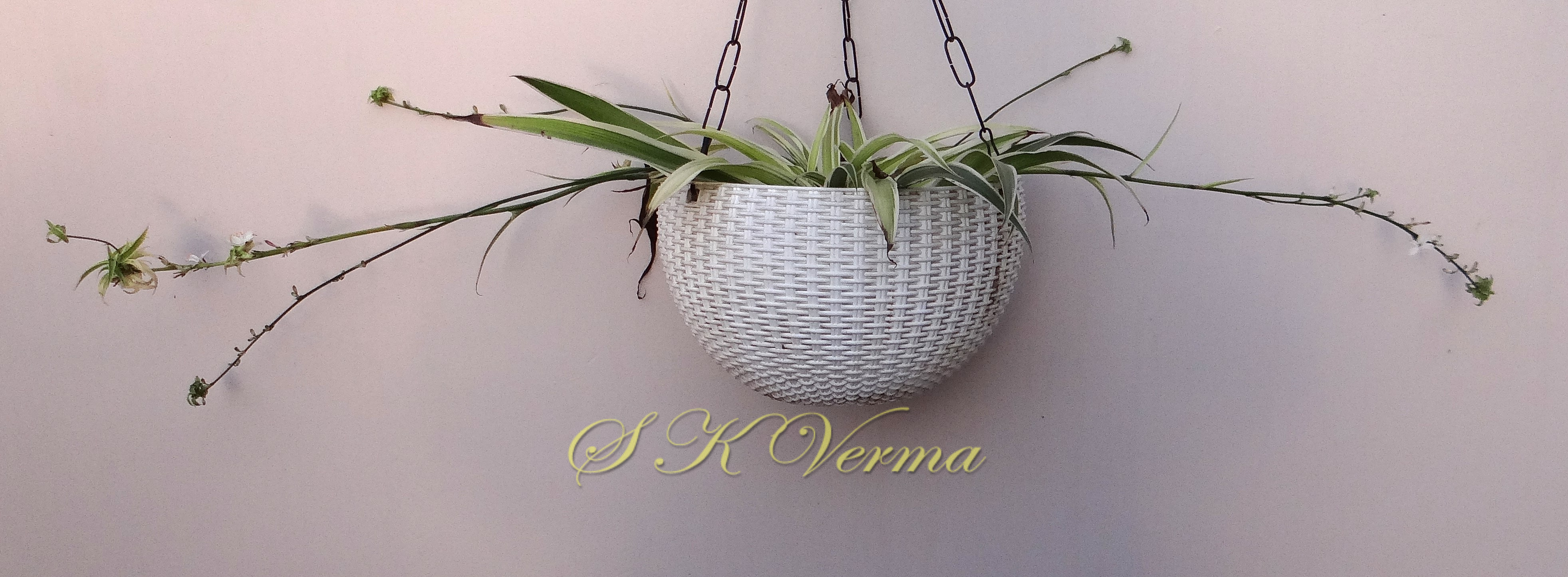
Chlorophytum comosum
Chlorophytum comosum
(Thunb.) Jacq., J. Soc. Imp. Centr. Hort. 8: 345. 1862; Fl. South Afr.; Fl. Zambesiaca; Fl. Trop. East Afr.; Anthericum comosum Thunb., Prodr. Pl. Cap. 63. 1794; Caesia comosa (Thunb.) Spreng., Syst. Veg. 2: 88. 1825; Cordyline vivipara Steud., Nomencl. Bot. ed. 2, 1: 419. 1840; Phalangium comosum (Thunb.) Poir, Encycl. 5: 252. 1804; P. viviparum Reinw. ex Kunth, Enum. Pl. 4: 607. 1843.
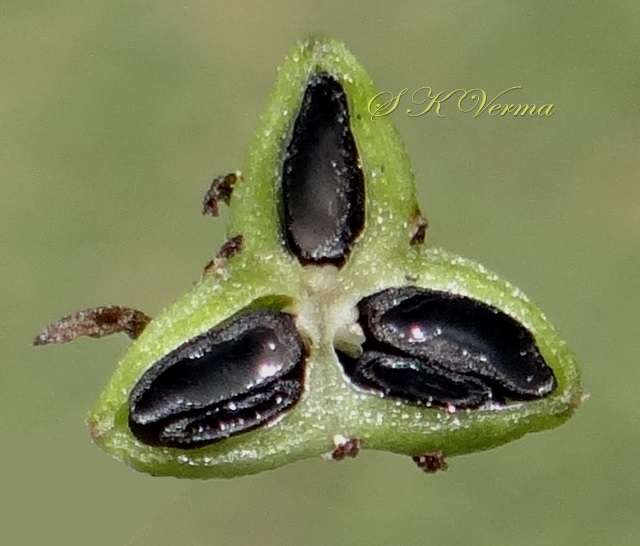
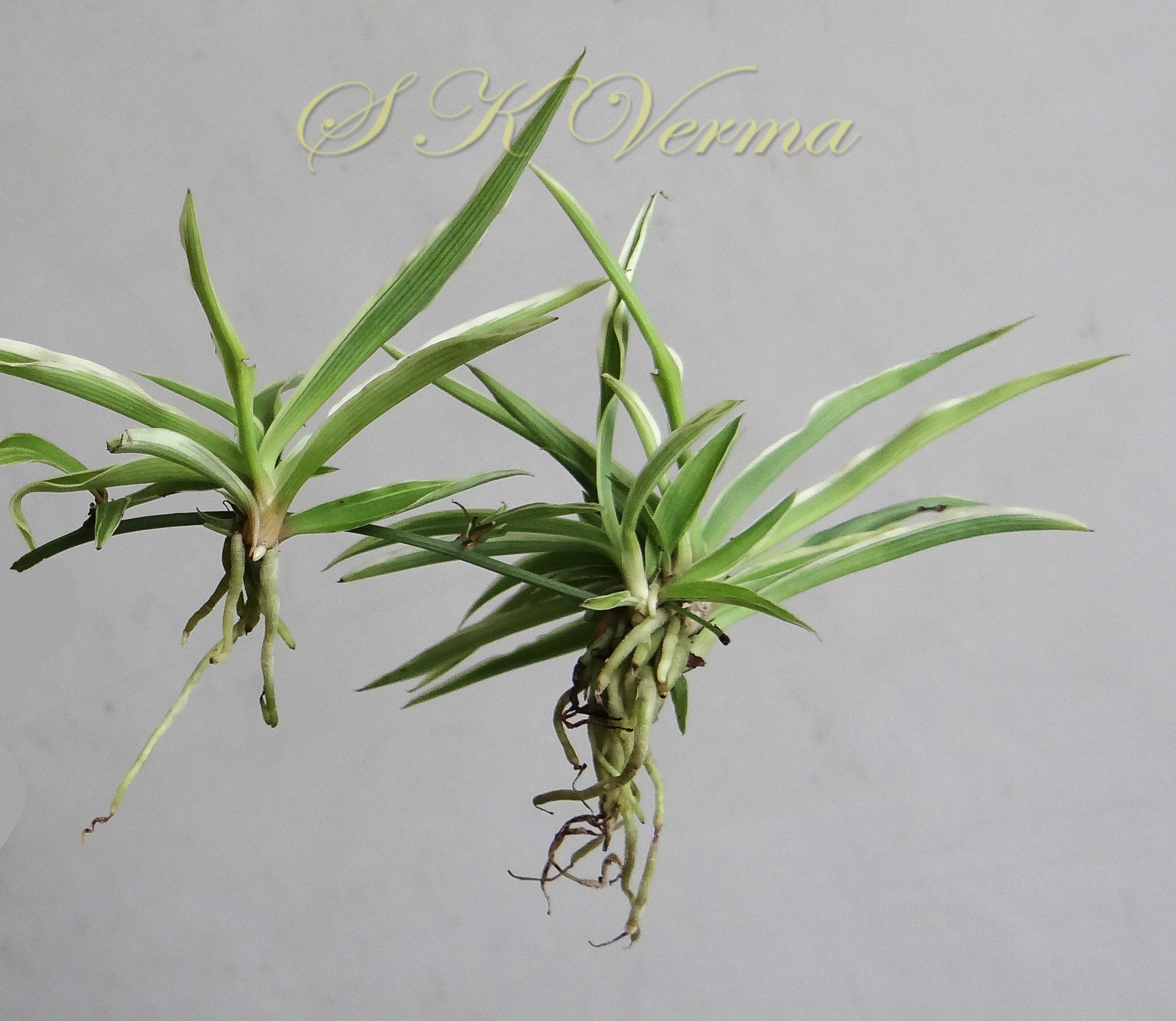
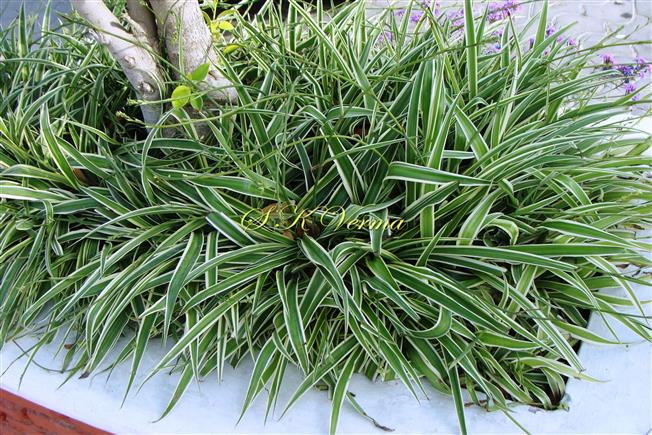
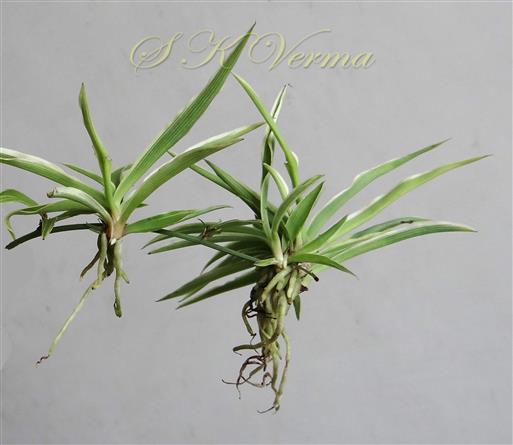
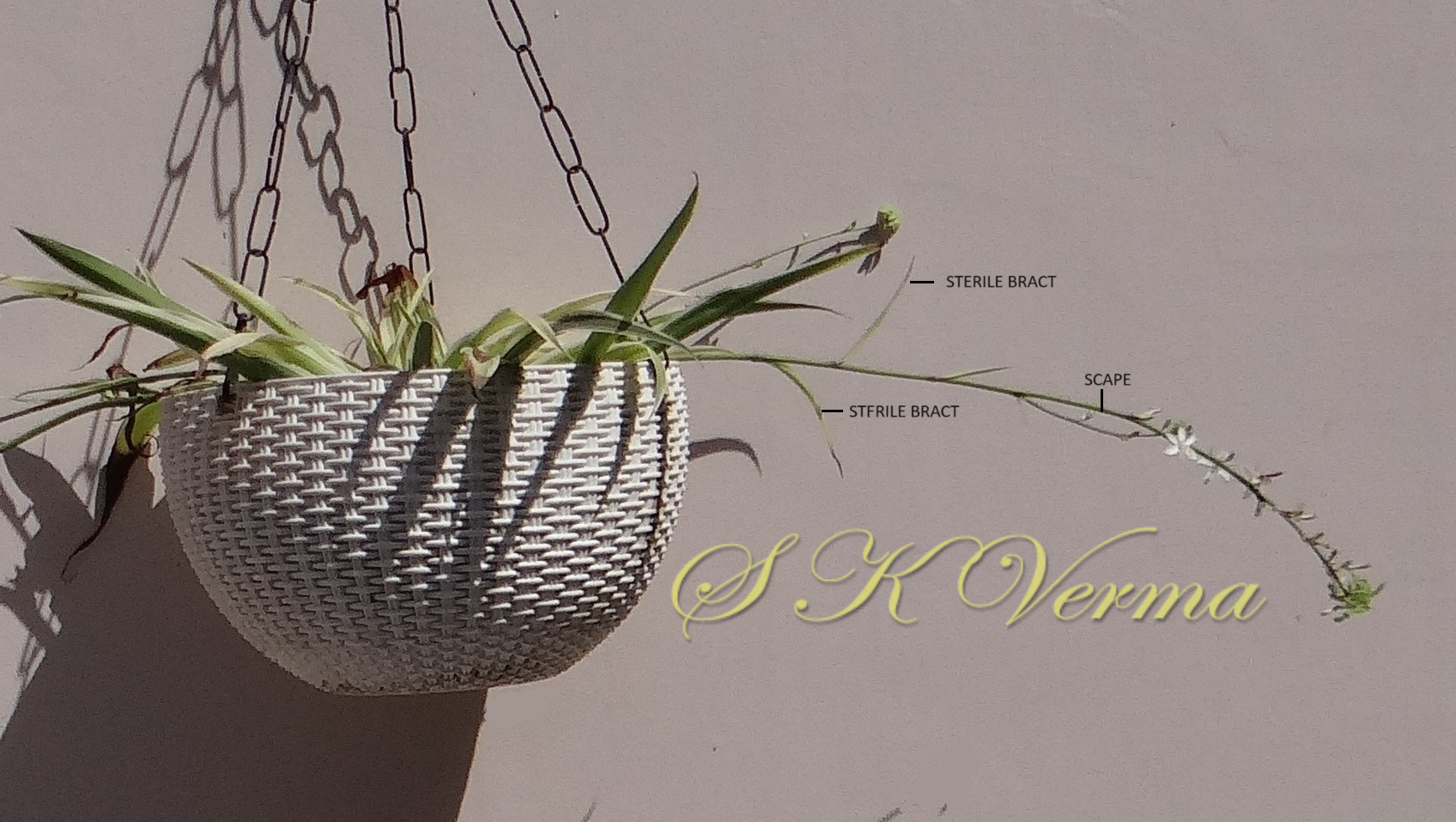
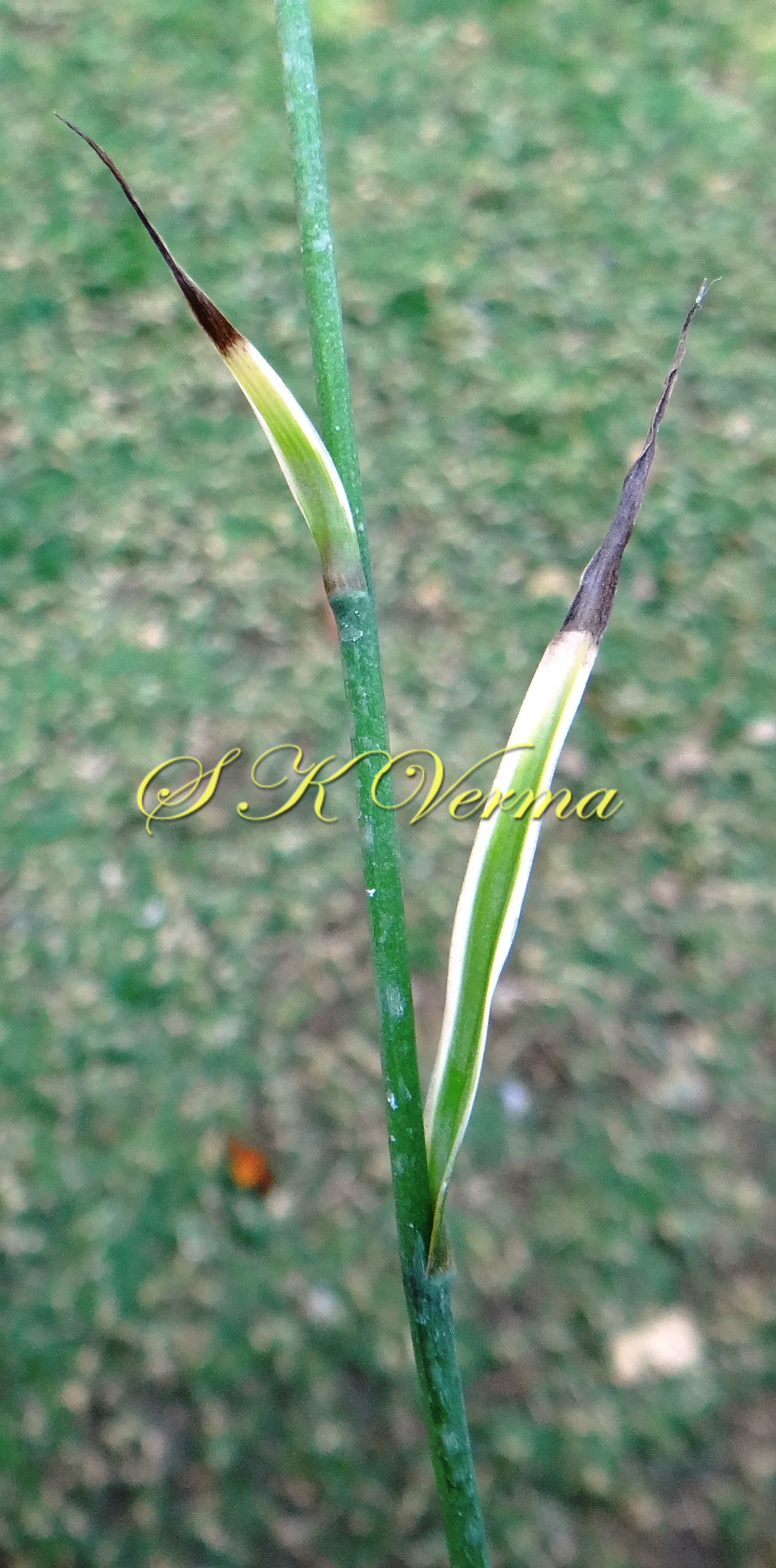
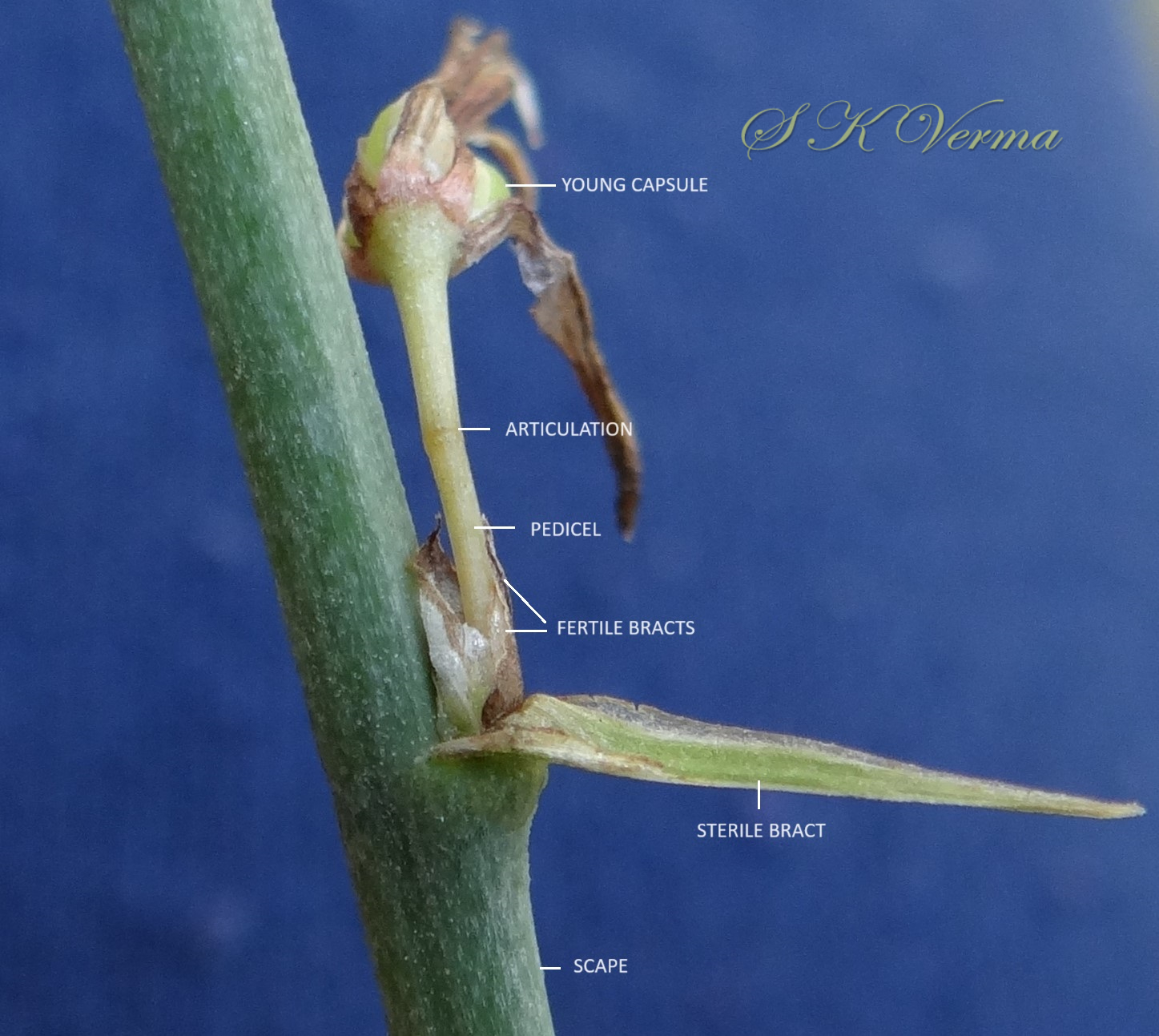
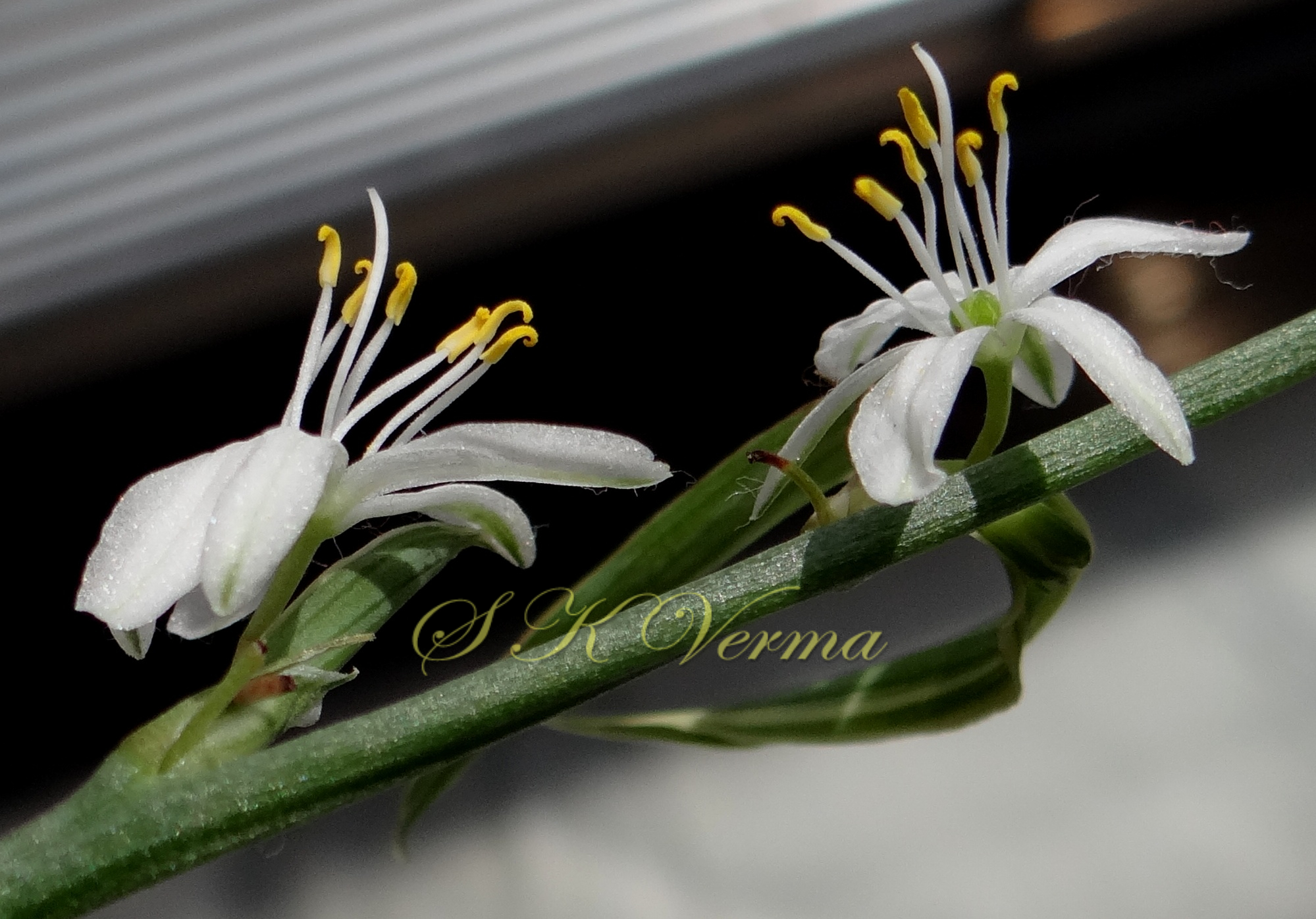
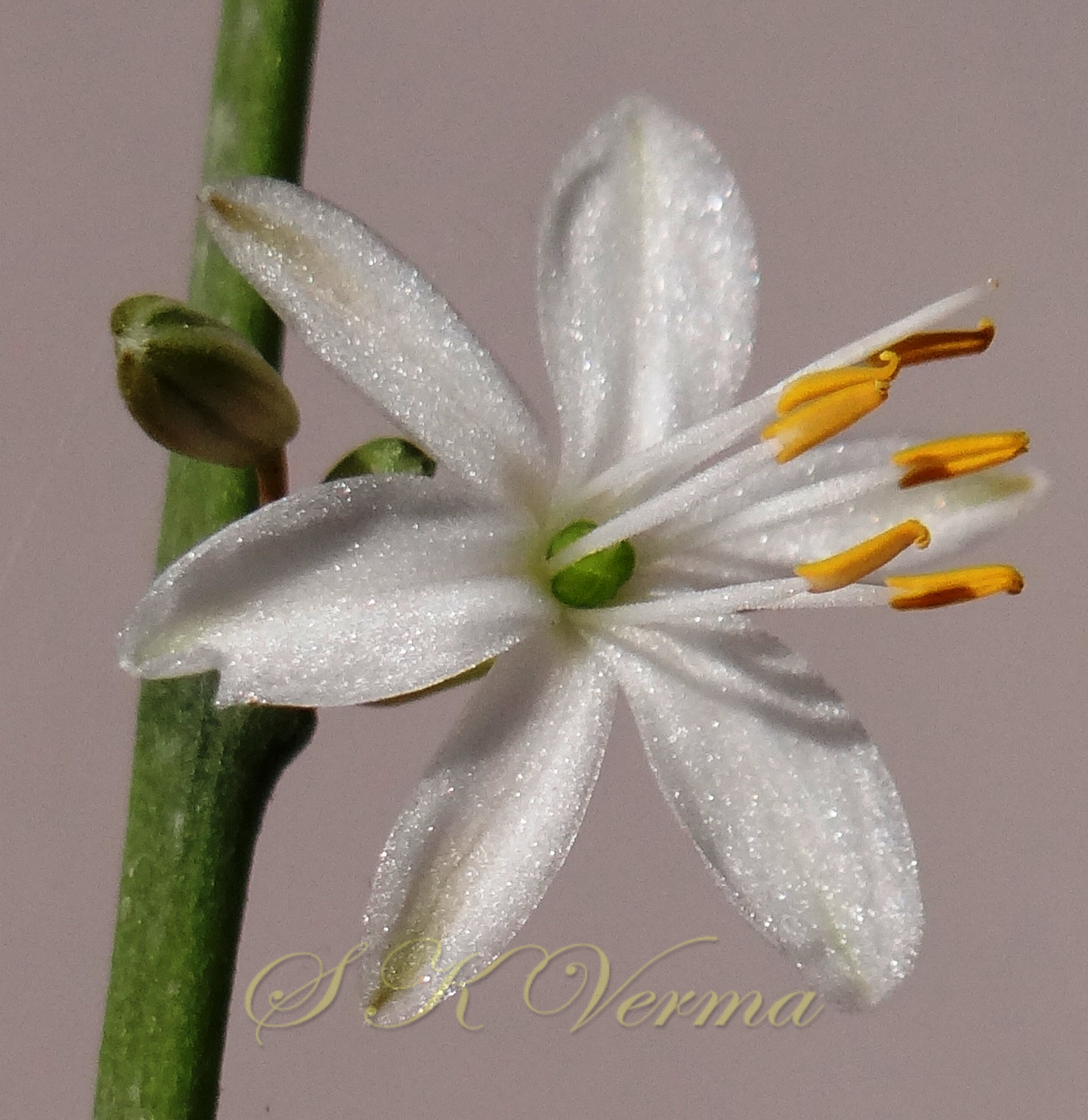
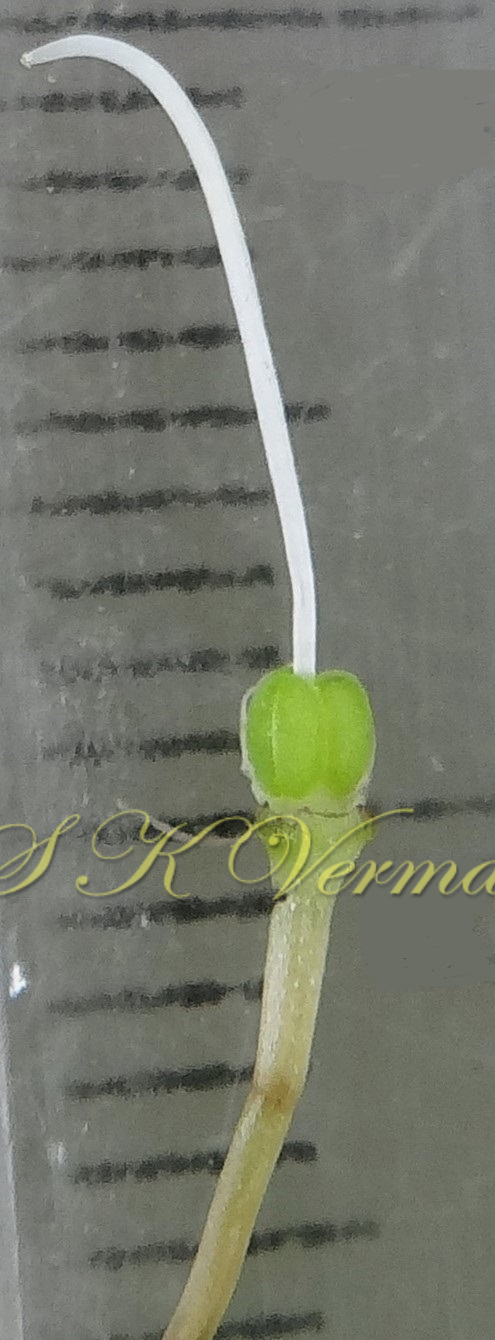
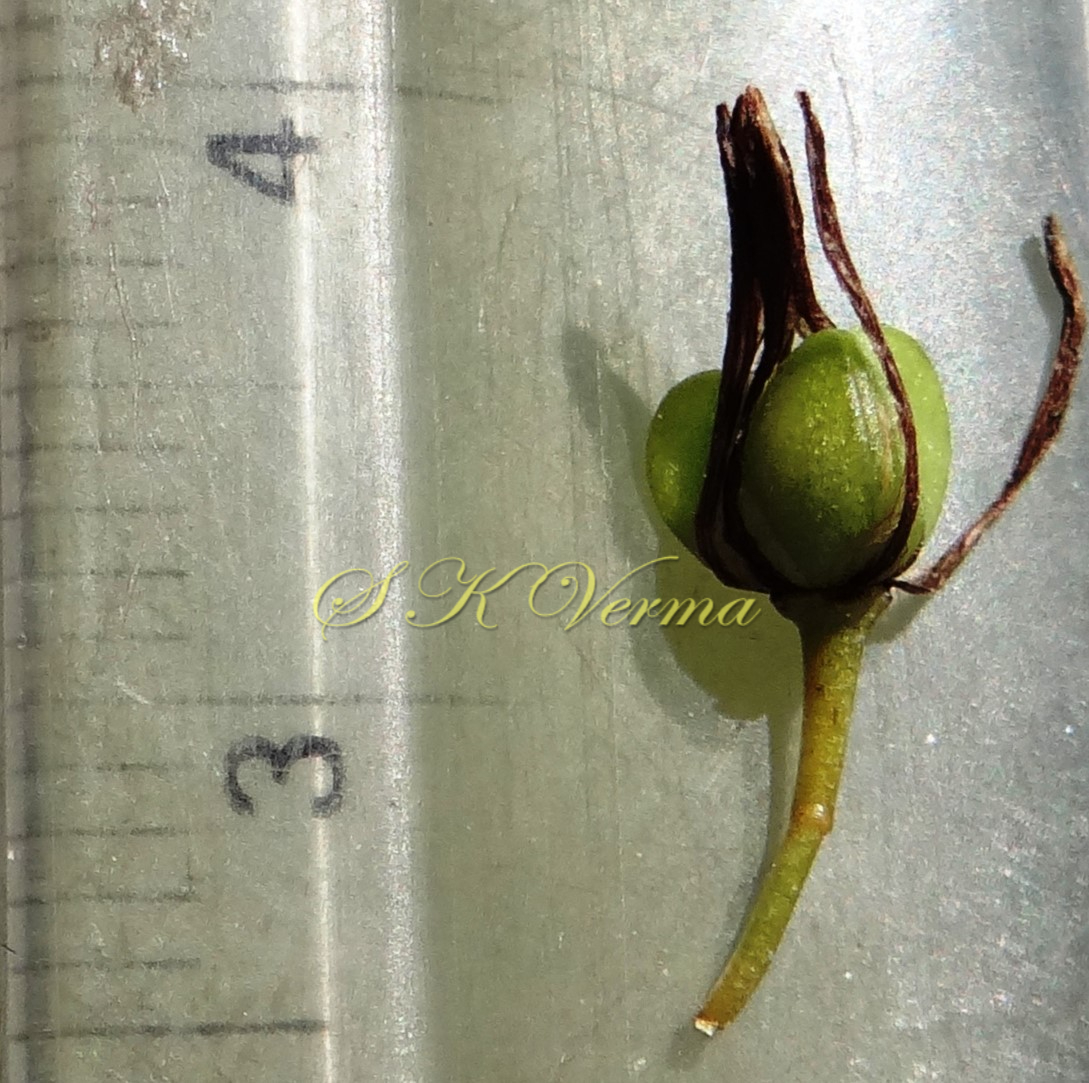
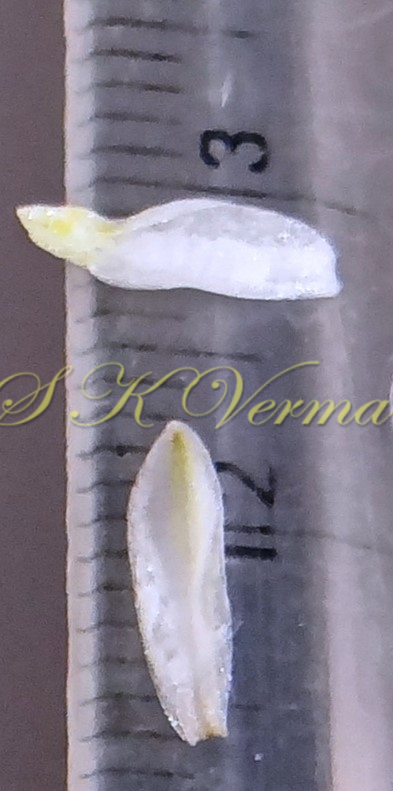
Tufted perennial herb, 15-70 cm high. Rhizome short, vertical, often indistinct. Roots narrow to slightly swollen, spongy, often with spindle-shaped tubers. Leaves in basal rosettes, pseudo-petiolate, lanceolate to strap-shaped, tapering at base and apex, 10-60 cm x 1-4 cm, margin entire or minutely scabrid, usually flat. Scape axillary, 10-75 cm long, longer than the leaves, sometimes with 1-2 basal ascending branches, terete, bracteate; sterile bracts (also referred as cauline leaves), narrow, lanceolate, 1.5-6.5 cm long, acuminate, fertile bracts small, deltoid, subulate. Flowers in racemose manner, often the apical flowers suppressed and bracts enlarged to form leafy tuft. Leafy tufts develop into new plants; new scape again formed in axils of new plants and this process can continue (a scape appears to have many new plants in succession). Pedicels thin, 4-8 mm long, articulated near the middle. Flowers bisexual, actinomorphic, star-shaped, hypogynous, in small, spiral, discrete, bracteate, axillary fascicles of 1-6. Perianth white, often keeled, greenish outside and apically, spreading or curved down; tepals 6, free, in 2 whorls of 3 each, subequal, 9-10 mm x 2.5-3.5 mm, oblong, tepals of outer whorl narrower than the inner. Stamens 6, exserted; filaments ca. 7 mm long, fusiform (usually slightly widened in middle), minutely papillate; anthers ca. 1.5 mm long, basifixed, curved apically, introrse, dehiscence by longitudinal slits. Ovary superior, sessile, +/- globose, 3-lobed, 3-locular, usually 4 ovules per loculus; style straight, sometimes geniculate near apex, nearly as long as or slightly longer than stamens; stigma minute. Capsule deeply 3-lobed, often bearing perianth remains, ca. 4-6 mm x 5-7 mm, dehiscing loculicidally by 3 valves. Seeds saucer-shaped, slightly folded, 2.5-3 mm, black.
Common Names: Spider Plant, Airplane Plant, St. Bernard’s Lily, Spider Ivy, Ribbon Plant, Hen and Chickens












-DSC01473.jpg)














-DSC01473.jpg)


